- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
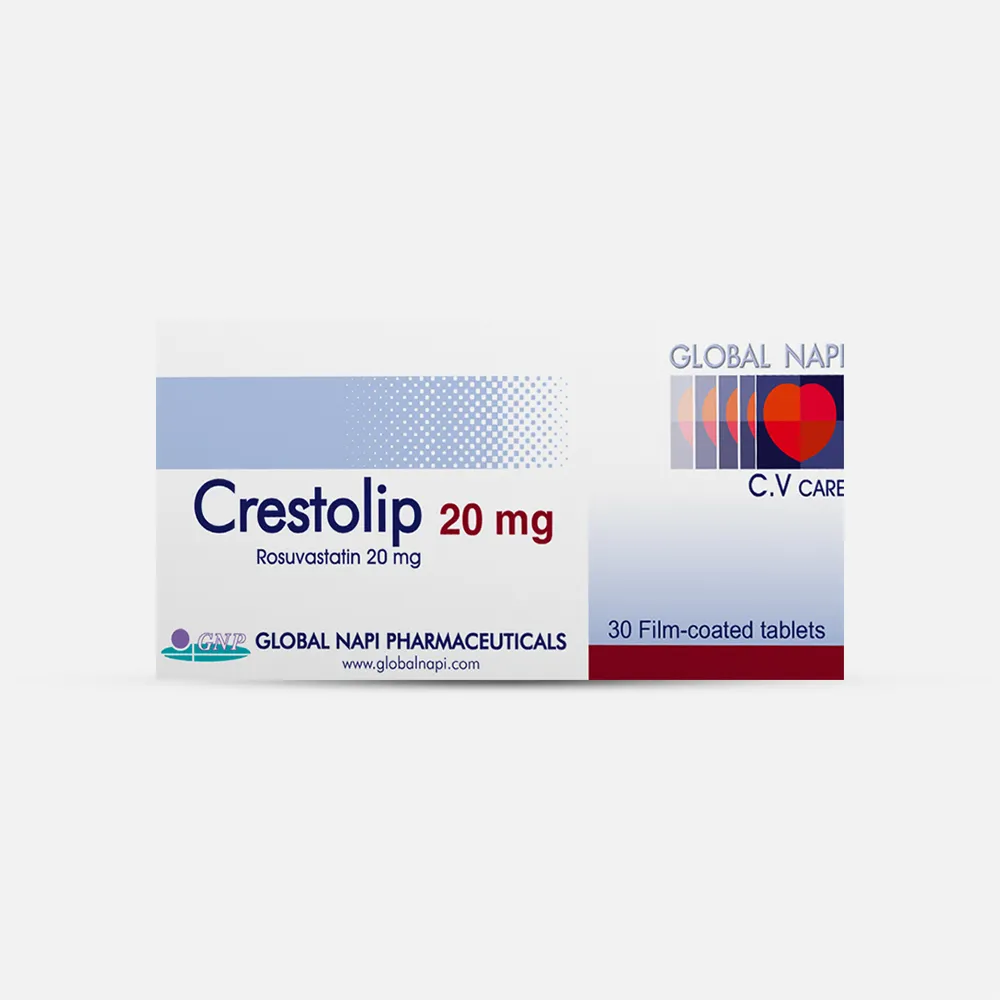
Product Description
Medical description
A lipid-lowering drug, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, used to treat high levels of harmful cholesterol in the blood and prevent cardiovascular diseases resulting from atherosclerosis.
Meaning and usage:
Prevention of cardiovascular disease due to atherosclerosis: Primary prevention: 1- Patients without diabetes aged 40 to 75 years with a blood LDL-C level of 70 to 189 mg/dL:
A- In patients with a 10-year risk of developing cardiovascular disease due to atherosclerosis = 5% to <7.5%: Moderate-intensity treatment: Oral: 5 to 10 mg once daily to reduce LDL-C by 30% to 49%.
B-In patients with a 10-year risk of developing cardiovascular disease due to atherosclerosis = ≥7.5% to <20%: Moderate-intensity treatment: Oral: 5 to 10 mg once daily to reduce LDL-C by 30% to 49%.
C-In patients with a 10-year risk of developing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease = less than 20%: High-intensity therapy: Oral: 20 to 40 mg once daily to reduce LDL-C by 50%.
Diabetic patients:
A- In patients aged 40 to 75 years without additional risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Moderate-intensity therapy: Oral: 5 to 10 mg once daily to reduce LDL-C by 30% to 49%.
B- In patients with a 10-year risk of developing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease = less than 20% or multiple risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: High-intensity therapy: Oral: 20 to 40 mg once daily to reduce LDL-C by ≥50%.
Patients with LDL-C level greater than 190 mg/dL and age ranging from 20 to 75 years:
High-strength treatment is used regardless of the calculation of the percentage of cardiovascular disease resulting from atherosclerosis or the presence of diabetes or not: High-strength treatment: Oral: 20 to 40 mg once daily Reduce LDL-C by 50%. – For pediatric doses and other doses in adult patients: See Dosage and method of use