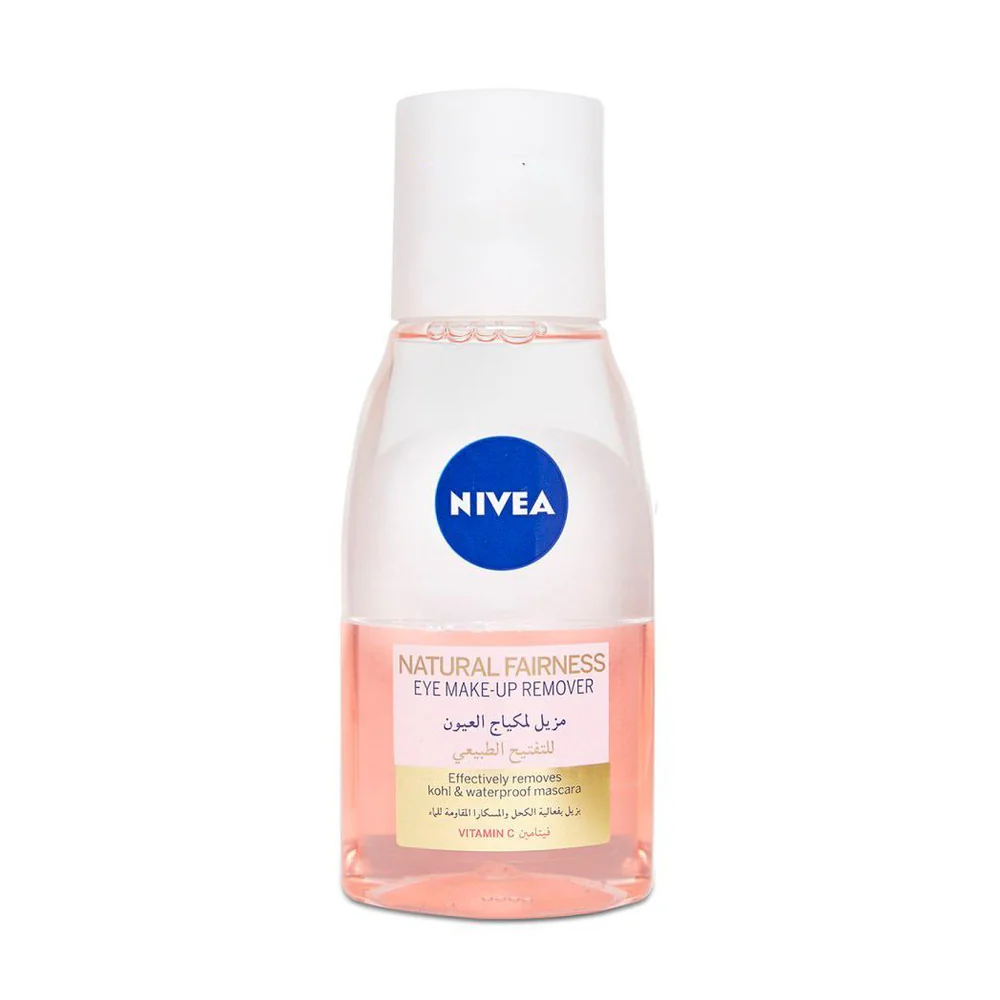
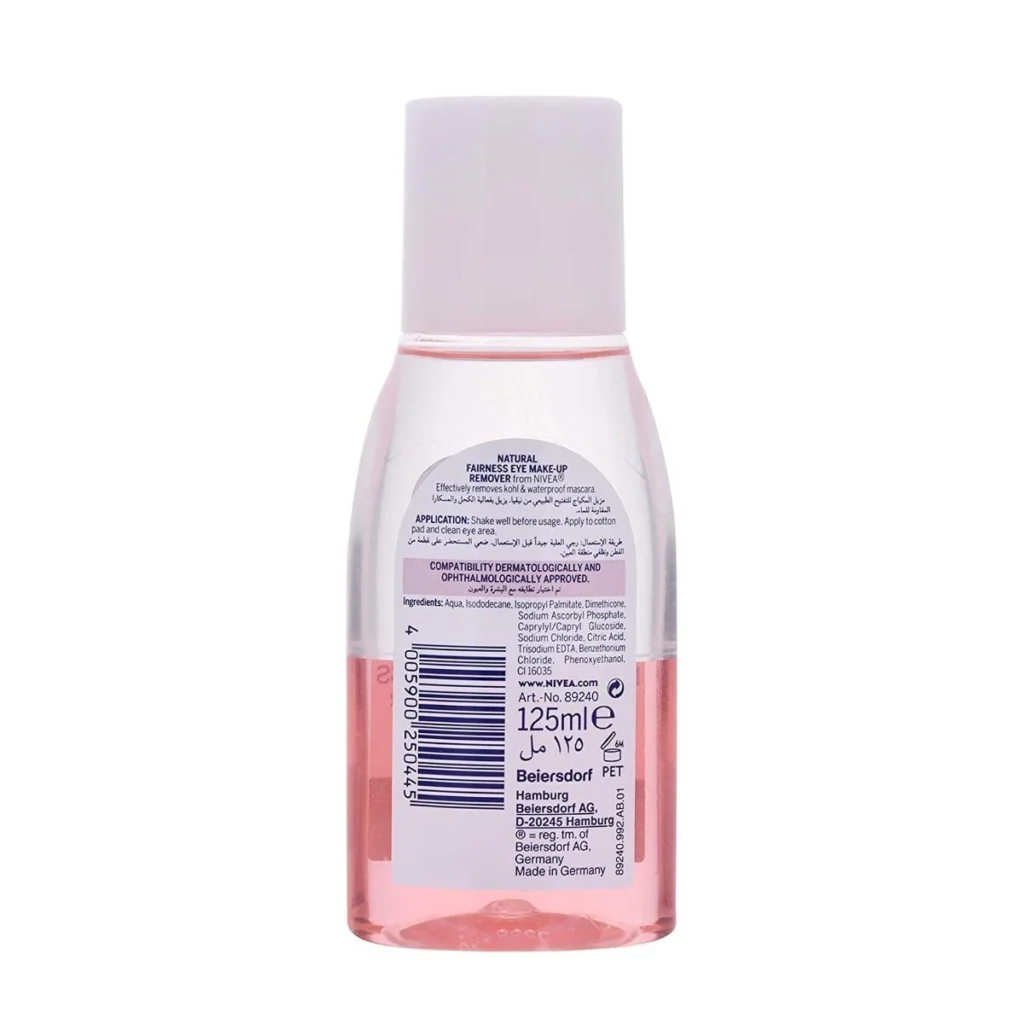
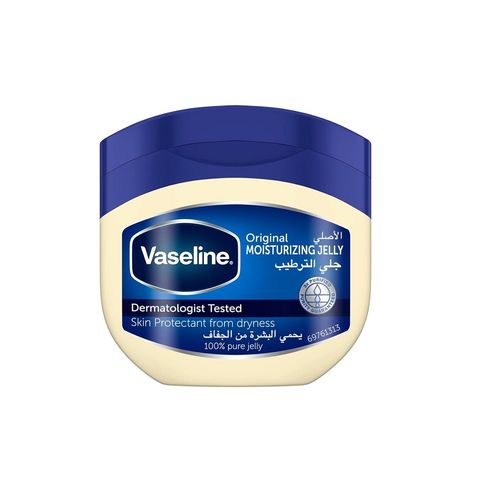
Additional information
Customer Reviews
Related Products

Useful Links
Categories
Contact Us
- 01090695200
- Ghaith Villa, Gomhouriya st. Mansoura
- contact@elembabypharmacy.com

© 2025 EmbabyPharmacy. All Rights Reserved.
Developed by: NAJ

Useful Links
Contact Us
- 01090695200
- Ghaith Villa, Gomhouriya st. Mansoura
- contact@elembabypharmacy.com

© 2025 EmbabyPharmacy. All Rights Reserved.
Developed by: NAJ